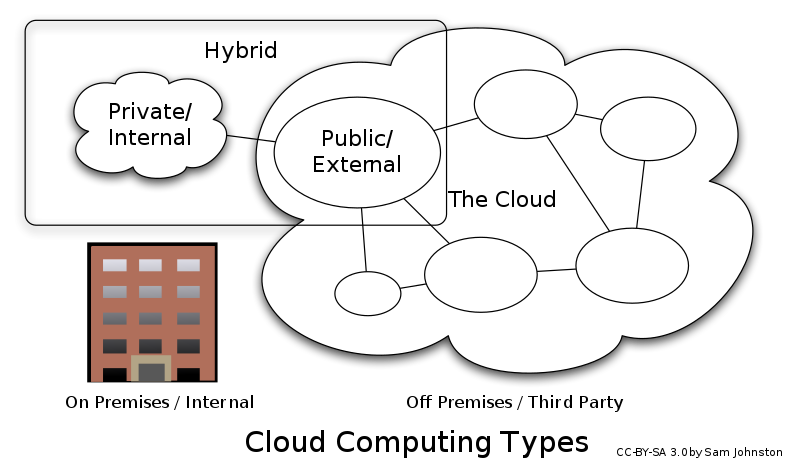
Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing
"This model of technology adapts to the needs of the company at all times, which only pay for what you use"
-Cost - Device and location independent
-Virtualization - Multitenancy
-Reliability - Scalability and Elasticity
-Performance - Security
-Maintenance
- Proven integration network services
- Services at world level
- A 100% infrastructure of cloud computing allows the content provider or services in the cloud without installing any type of hardware, since it is provided by the supplier of the infrastructure or platform in the cloud.
- Implementation faster and with less risk.
- Automatic updates that do not negatively affect it resources.
- It contributes to the efficient use of energy.
- Centralization of applications and data storage creates an interdependence of service providers.
- Application availability is tied to the availability of Internet access.
- "Sensitive" data of the business do not reside in facilities of the companies, which could result in a context of high vulnerability to the theft or theft of information.
- The reliability of the services depends on technological and financial "health" of cloud service providers.
- The availability of highly specialized services could take months or even years that they are feasible to be deployed in the network.
- Functional maturity of applications that they are continuously modifying its interfaces, so the companies of non-technological orientation learning curve has a significant pending, as well as automatic consumption by applications.
- Security.
- Scalability in the long term.

1 comments:
- Lisa Jay on August 19, 2020 at 2:28 AM said...
-
It was the first time my granddaughter came to me and confided about her battle with oral and genital herpes and her self destructive thoughts.
A gaping vacuum of fear and love opened inside me. I knew what it felt like for her to be in such a situation. But after hearing how someone I loved so dearly struggled I have no option but to promise her help. I wanted to help in all possible ways. I sought counsels from an old and experienced nurse whom I've known to deal on natural herbs because I believed in nature. After hearing from me she smiled and before I could say another word she replied me there's cure but natural herbs. I don't care as long as my child is cured! I shouted. She told me about a doctor in Africa who has cured people of herpes. She gave me his email drutuherbalcure@gmail.com ,I contacted him immediately and then ordered medicine for my child which he sent through the UPS courier to me. My daughter started medication and the next day her mouth sores were physically healing and she told me it's working and within four weeks she testified to me that she was cured! I've always believed that nature has cure for any diseases and I'm happy to tell everyone my child is cured.
Six months later we went for another test to be sure and here is the result,
Six months after medications;
Her hsv1&2 test results;
Igm - 1.49
IgG - 0.36
She don't have any symptoms again and has moved on happily and is now in a serious relationship with her fiancee -